Features
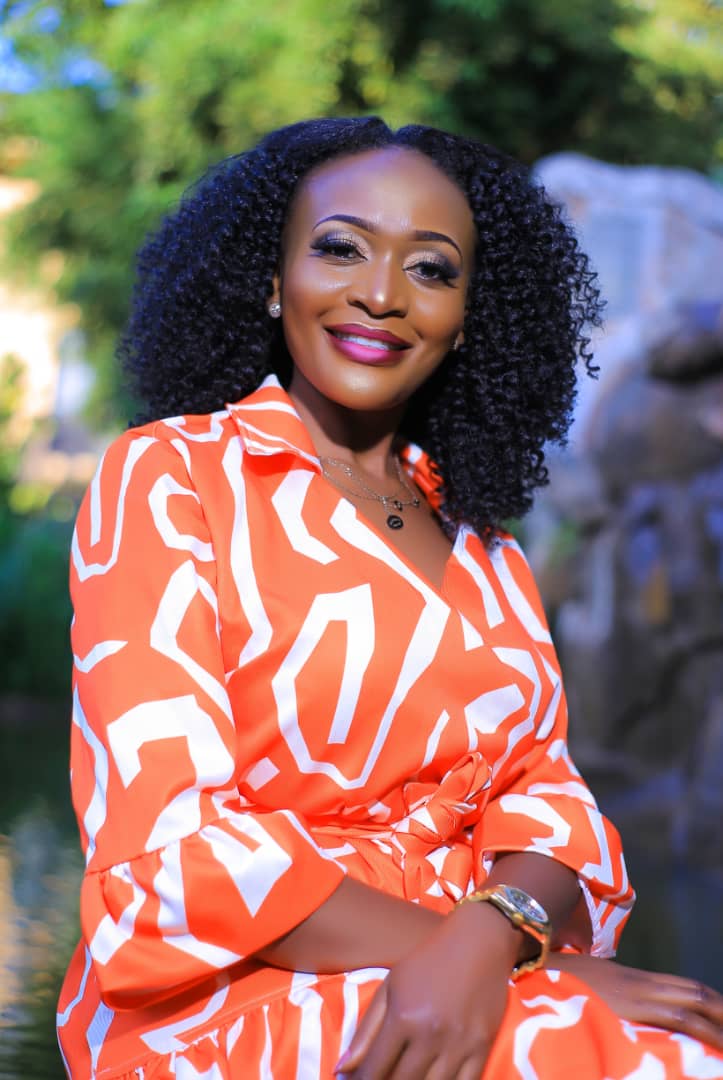
Laetitia Mugerwa: Challenging the Juvenile Correction System in Uganda
If Uganda shines a light on what happens inside the jails, the world will know the truth about every nation.
In one of his remarkable speeches, Nelson Mandela said that “No one truly knows a nation until one has been inside its jails.”
Mandela had spent 27 years split between Robben Island, Pollsmoor Prison, and Victor Verster Prison after he was sentenced to life imprisonment for conspiring to overthrow the state, following the Rivonia Trial. This profound statement – coming from one of the most resilient patriots that ever lived – isn’t just a fact from history, it is a lived experience only known by those that have ever been imprisoned.
It’s often said that prison is a black and white story where there are no in-betweens. One is either bound to transform from bad to good or bad to worse. The first time I made a prison visit, I didn’t believe that there are good people in prison. Growing up, I was always told how every evil person was destined for prison. It was not until I met Nankya that my entire perception of prisons changed. Nankya was a 14year old girl who was detained in cells after she was arrested together with a gang of young boys who were in possession of drugs.
Nankya narrated to me her entire ordeal and how she ended up in cells. Days before her arrest, a man had been gang robbed and beaten to death. Although the perpetrators of the crime were not found, police launched a crackdown on idlers and groups of teenagers they suspected to have been involved in the murder. Nankya was in the wrong place at the wrong time at the time of her arrest. After the interrogation of suspects, it was discovered that one of Nankya’s friends had been involved in the murder.
Efforts to prove Nankya’s innocence and distance her from the scene of the crime fell into thin air. She was detained at the cell for days that later turned into weeks. By the time I met with her, she had spent 3 weeks at the cells. She told me how life in the cells had changed her a lot. She also revealed that the first days were like living in her worst nightmare. The fact that she was still young and imprisoned among adults was very haunting. All the female adult prisoners treated her with such cruelty. For a good number of days, Nankya had to endure the stench of the toilet as she was forced to lay her head just meters next to the toilet.
“Every time someone was using the toilet, I had to wake up and wait for them to finish, then I was told to clean up” she narrates. It was inexcusable not to compile with the orders of the ‘King’. King is a code used to address the leader within a cell. She commands respect and her orders are the law within the cell. When I asked why this went on for such a long time without her reporting it to the cell authorities, Nankya informed me that any attempt to report to the authorities would definitely land one in hot soup. Firstly, the king always conspired with some of the prison guards who she used to bribe quite often.
When I asked her about her parents, Nankya didn’t disclose much. She said “I don’t have parents, in fact, I don’t remember having parents at all. I was brought up by my maternal grandmother. She told me that my mother died in the early days of my life and no one ever knew who my real father was”.
Studies by Chance for Childhood in Northern Uganda indicate that 60% of children are apprehended for petty crimes (e.g. theft of food, school materials, and sanitary pads). Petty crimes in Uganda can be punished harshly by the authorities. Far too often, children are sent to adult cells where they are subject to sexual, emotional and physical violence, including appalling conditions.
The continuing nonexistence of probation officers and prosecutors implies that children are continually held in prison for long periods of time. When a hearing is finally held, only a minority of children are granted the right to be tried in a juvenile court with proper legal representation.
A severe shortage of social workers, judiciary personnel and pro-bono lawyers undermines children’s rights to access fair and legal attention and protection. It is prudent to note that where there is no prospect of rehabilitation, children risk leaving detention facilities very traumatized. Current reoffending rates are 32% and protracted unlawful detention in adult prisons, even for petty crimes, is widespread in Uganda.
Surveys conducted in Uganda amongst children that had been arrested at least once in that year in Agago showed that for girls, attempted suicide and burglary was the main reason given for their arrest. For boys, assault, petty theft, and defilement were common. With regard to defilement, other reports indicate a high prevalence of 1256 juvenile offenders between 2011/12 and 785 (63%) were accused of having committed defilement.
If Uganda shines a light on what happens inside the jails, the world will know the truth about every nation.