Features
How Should We Tell The African Story? – A Conversation with Ukamaka Olisakwe
This is how to tell the African story: tell all.
Editor’s note: This interview with Ukamaka Olisakwe was one filled with laughter and very important storytelling nuggets. We often talk about telling African stories but we do not talk about how many African women are overlooked in these stories. The voices of men are more amplified and they are commonly chosen as experts or important voices in conversations. Ukamaka, the founder of Isele Magazine and author of Ogadinma, is described as a ‘Nigerian feminist author’ whose works focus on women, motherhood, childbirth, and postpartum depression. Here, Ukamaka and I discuss the important role the literary community is playing in telling African stories, what it means to include women when we tell stories and why it is important to acknowledge and amplify women’s voices and works.

Ukamaka Olisakwe could be anything – a computer scientist or senior banker, but she chose writing. When I asked her why, she broke into fits of laughter: “I talk too much.”
Ukamaka, author of Ogadinma and founder of Isele Magazine, loves to be called Uka. Her imaginations are wild, she is always restless with ideas, and her mind is filled with thoughts of how to get things going. She studied computer science in school and worked in a bank for 7 years. There, she shared her thoughts with her colleague and friend so often that her friend asked her to document the things she talked about. Until then, Uka wasn’t so keen on storytelling and writing, “I didn’t see it as something that is very successful,” she said. But she decided to give it a try, anyway. Through the years, Uka has worked so hard by contributing her quota to the Nigerian literary scene. Now, she’s a force. She no longer sees storytelling as something unsuccessful. She sees it as “a reflection of our society.”
Once, on my way home from work, a man, whom I had a conversation with tried so hard to convince me that God did not naturally give the black man sense. “My sister,” he said “don’t let us deceive ourselves, God dash oyinbo people sense pass us.” I stared at him in pity, but I wasn’t surprised that a black man would think so little of himself and his race. I tell Uka this story.
“Such thoughts and ideas came from what we are fed,” Uka said, “There’s often this idea that there is someone out there who is smarter than us. Someone out there who should curate our stories, and guide us on how to be. It started with colonialism, you know, bringing us things – like religion for example – and demeaning our religion. A kind of hierarchy was created, and people who are naturally good began to question their skills, intelligence, and smartness. Everything is now in relation to whiteness, and western civilisation. There’s now ‘oh, how smartly do I dress? If I’m wearing this, I’ll fit well into a particular system, but if I’m wearing my buba and iro, I won’t be smart and be considered uncivilised or bush.’ There’s this hierarchy and supremacy we’re battling. That’s where storytelling comes in. It helps us to dismantle and destroy that notion. When people tell a story about themselves, they are not just talking about a situation, they’re telling you what formed them, who they are, how complex they are as human beings, their society, their family unit; everything.”
Even for Africans, telling the African story is not just about putting pen to paper. It is also about who gets to write what and how, because the words you write are a reflection of how you see yourself, your race, your world.
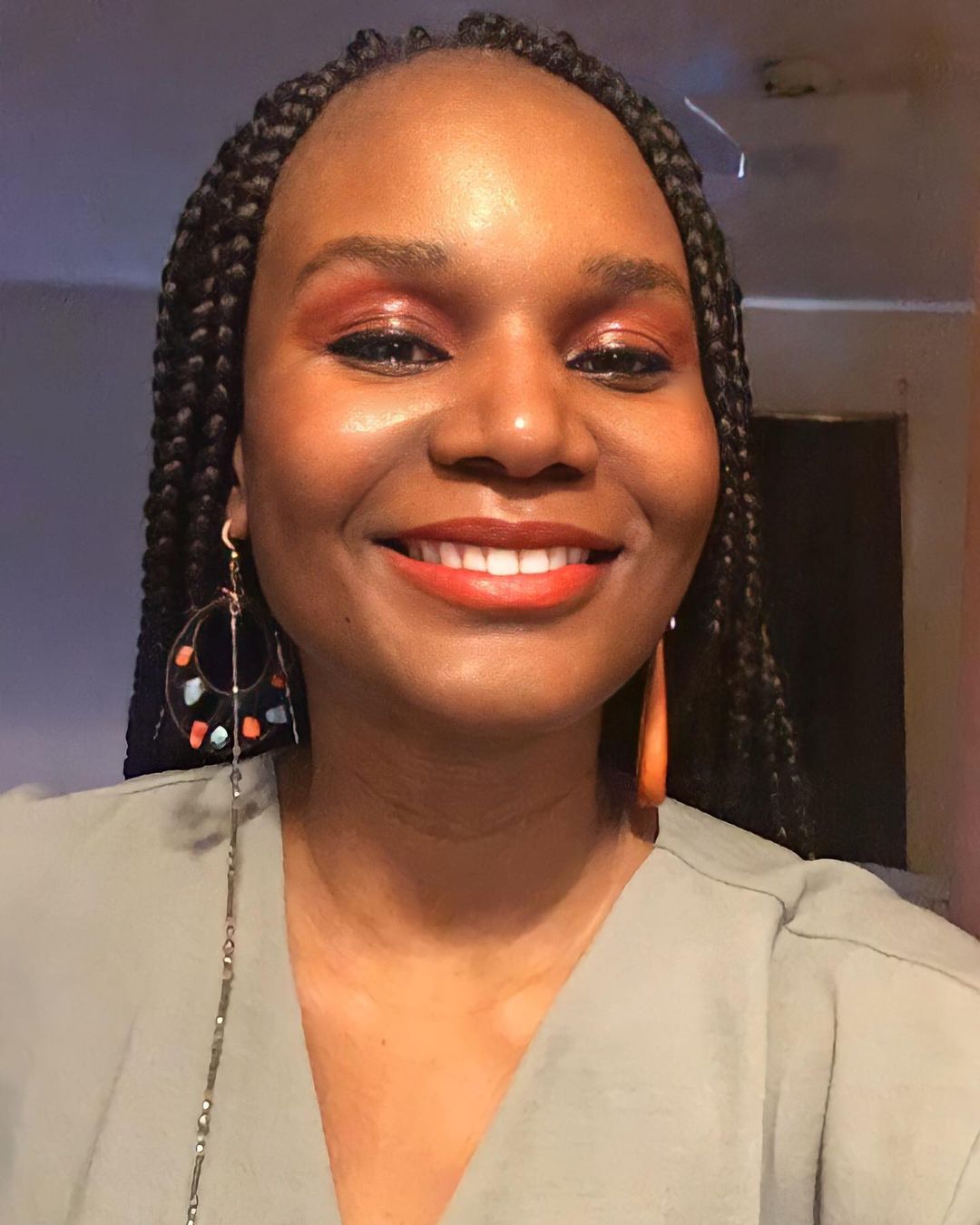

In 2011, Ukamaka published her first story, Girl to Woman. The story was so well read that the owner of the magazine said he was going to buy her lunch. That gave her the encouragement she needed to tow the writing path. “I needed that validation, that support. I needed people – outside of my friends, people in the literary space – to say ‘yea, there’s something Ukamaka is doing that we find really interesting.'”
From writing Girl to Woman to Ogadinma and founding Isele Magazine, Uka is interested in stories that hyper-focus on the self “because from there, you get to see the person’s relationship with their society, you get to see their relationship with their community, even in the public compound where they live. You see the bits of the little things that come together to make us who we are. And then when you blow it up on the national scale, you get to see that the little things that formed us into who we are decided how our politics is. That’s where you get to see our insecurities, diligence, love, our betrayal – everything that makes us human.”
And that is why who gets to tell the African story is equally as important as the stories we tell. For Uka, it is simple: when it comes to deeply personal things, you should be immersed in that world for you to be able to do justice to that story.
There’s a difference between when an observer writes a story and when people write stories of themselves. The latter, Uka said, starts from the self to the situation, but the former sees them as sociological work, anthropology, or research. One is deeply emotional. In the other, there’s a detachment, an abstraction. So it is important to ask yourself if and why you are the right person to tell the African story.
“Why do you want to tell African stories?” Uka said, “If you’re not African, why do you think you’re the right person to tell this story? Could you have collaborated with the people you’re writing about to tell their stories? Or are you writing from the observer’s gaze, seeing the subjects as a sociological work or anthropology; researching them, writing about them and their situation, not their individual lives? That’s what happens when you write as an observer. Observers write about the situation and the political nature. That’s where they include statistics, research, quotations from what other people have said. But when individuals write about themselves and their situations, they start from the self to the situation. When I write about EndSARS, for instance, I can write personal stories – maybe falling in love during the protests, or how the protests affected my family and friend. There’s a difference: there’s an abstraction, a detached way of narrating about these people because you’re observing them, and then the other is personal, deeply emotional.”
Telling the African story – as someone who is not African, does not live in Africa, and does not live the experiences of Africans – is akin to a man writing about a woman giving birth and going through postpartum complications, “what tool do you have to be able to tell these stories? What experiences have you gathered?”
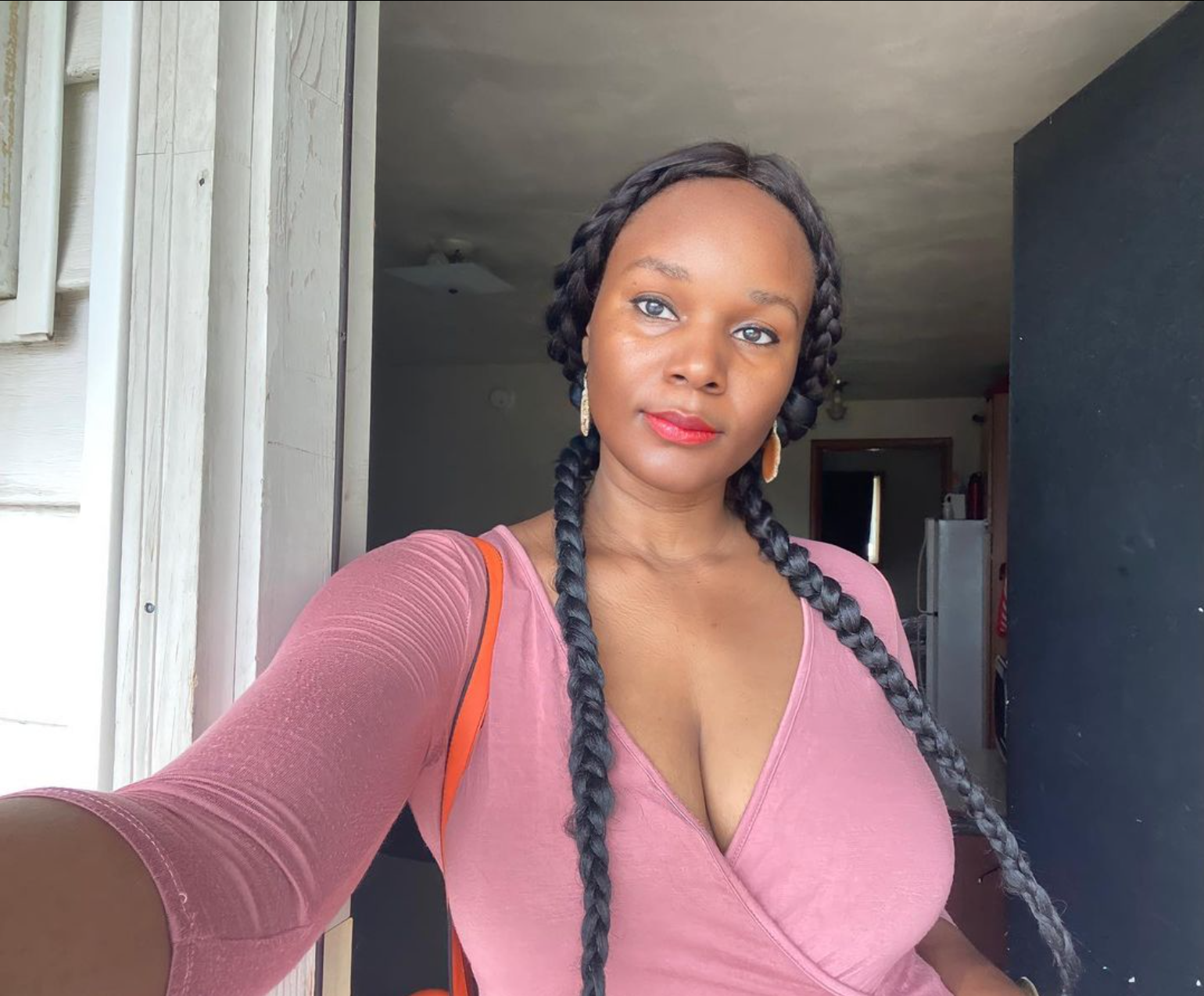

Stories form us. And African stories are so diverse and populated by complex characters who can’t be squashed into a single story. Trying to fit the billions of people into one story is how stereotypes are borne. It is how we cook the narrative of helpless and hopeless black humans who must need the western world to survive, and feed these narratives to people who then regurgitate the same narrative to generations after them.
Stereotypes become self-fulfilling prophecies. It is, thus, important to amplify the voices of millions of African storytellers holding a mirror to our society and telling our stories in ways that resist categorization. That is what Ukamaka is doing with Isele Magazine.
“That’s what literary magazines are doing; dismantling stereotypes. When you submit your work to a magazine, they expect a particular kind of story from a particular kind of people. They expect all stories that come out of Africa to be politically natured. They expect you to address politics, neo-colonialism, religion, or whatnot. Unlike, say an American writing about high school girls or sex in high school. The goal for me, at Isele Magazine, is to tell these diverse stories about people. At Isele, we give the playing field for people to tell any kind of story. Even the kind of stories other people would call mundane. Our contributors are writing amazing stories; they are paying attention to even those little details in our community.”
Many African authors have been accused of writing stories that pander to the western world in a bid to get published, grants, or win prizes. ‘Trauma porn,’ it is called. But isn’t that their reality? Shouldn’t they write about a home that takes and takes and gives them almost nothing in return? Or a culture that comes for their throat? Or about a land where the milk has gone sour and the honey has dried up?
“It was in the early 2000s that the words ‘trauma porn’ became a thing. Certain writers were accused of writing trauma porn, and I did find the criticisms unfair because those people who were writing those stories were writing personal experiences. The beauty of storytelling is that people can tell different and diverse stories; if one’s person’s story is too trauma heavy for you, there are other writers who are doing something entirely different. We have someone like Suyi Okungbowa who does a fantastic job writing speculative fiction which is not about trauma.
Balancing African stories starts with publishing different voices, having a dashboard of different themes, genres, and stories combating each other for space. For instance, when a reader goes through Isele Magazine, they get to see different textures of stories. Readers can easily move from a story about pain and loss to one of sex and lust.”
Isele Magazine is working on publishing its first print anthology. They’ll also have yearly prizes where they award short stories, essay writers, and poets. Next year, they’ll introduce the Isele Book Prize where African writers who are doing amazing things in the field would be acknowledged and appreciated.
From Isele Magazine to Lolwe, Doek, The Shallow Things Reviews, we have so many literary magazines shaping Africa’s literary scenes and publishing diverse stories. It is time to give them their flowers. “When we talk of balancing stories, we must also realise that writers need to eat. To have a balance, we must be willing and able to pay writers who will write them. That’s why we need to create a supportive environment for literary magazines so we can survive. A lot of literary magazines don’t get funding. A few donations here and there but the funding isn’t there, we do this work with our personal money.”

Ukamaka Olisakwe is a storyteller through and through; Ogadinma and her many other works are proof. Like Buchi Emecheta on whose shoulders she stands, Uka’s works focus on women, wifehood, motherhood, childbirth, postpartum interiorities, amongst other things. Ogadinma is a story of a woman’s journey to independence. Thankfully, many women have attained a certain level of literary independence.
“You know they used to call women’s literary works ‘domestic fiction’ but when the men write their global political stories, they’re considered high literature.
I want to believe now that the balance has been tilted to our favour because we have lots of women telling our stories. And they aren’t just telling stories about family, they’re telling diverse stories and coming from all angles – women writing horror, romance, erotica, contemporary city stories, writing about being women and mothers, they’re redefining what literary fiction is. Their works can no longer be dismissed as unserious. There’s no one serious way of creating change in your community. There’s no one serious way of writing.
When you look back – at the Chinua Achebe African writers set, there weren’t many women represented that period until the likes of Flora Nwapa, Buchi Emecheta. We didn’t have that much representation, even in the past, you’d hear some things like ‘the patrons of Nigerian literature’ and you’d see people mentioning the likes of Wole Soyinka and Chinua Achebe – who I consider African literature gods, by the way. The representation of women started coming much later with Buchi Emecheta coming into the scene. And then in the 2000s or even the late 1990s, we started having the likes of Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie, Lola Shoneyin whom I adore, Chinelo Okpara, Chika Unigwe – women who are doing amazing and putting in that much work.”
Independence, for women storytellers, is having their voices and works acknowledged. Like Ukamaka who has books coming out – one of them being a literary romance novel, and many others in the literary space, women are putting in the work, and tooting their horns. What a time to be alive!
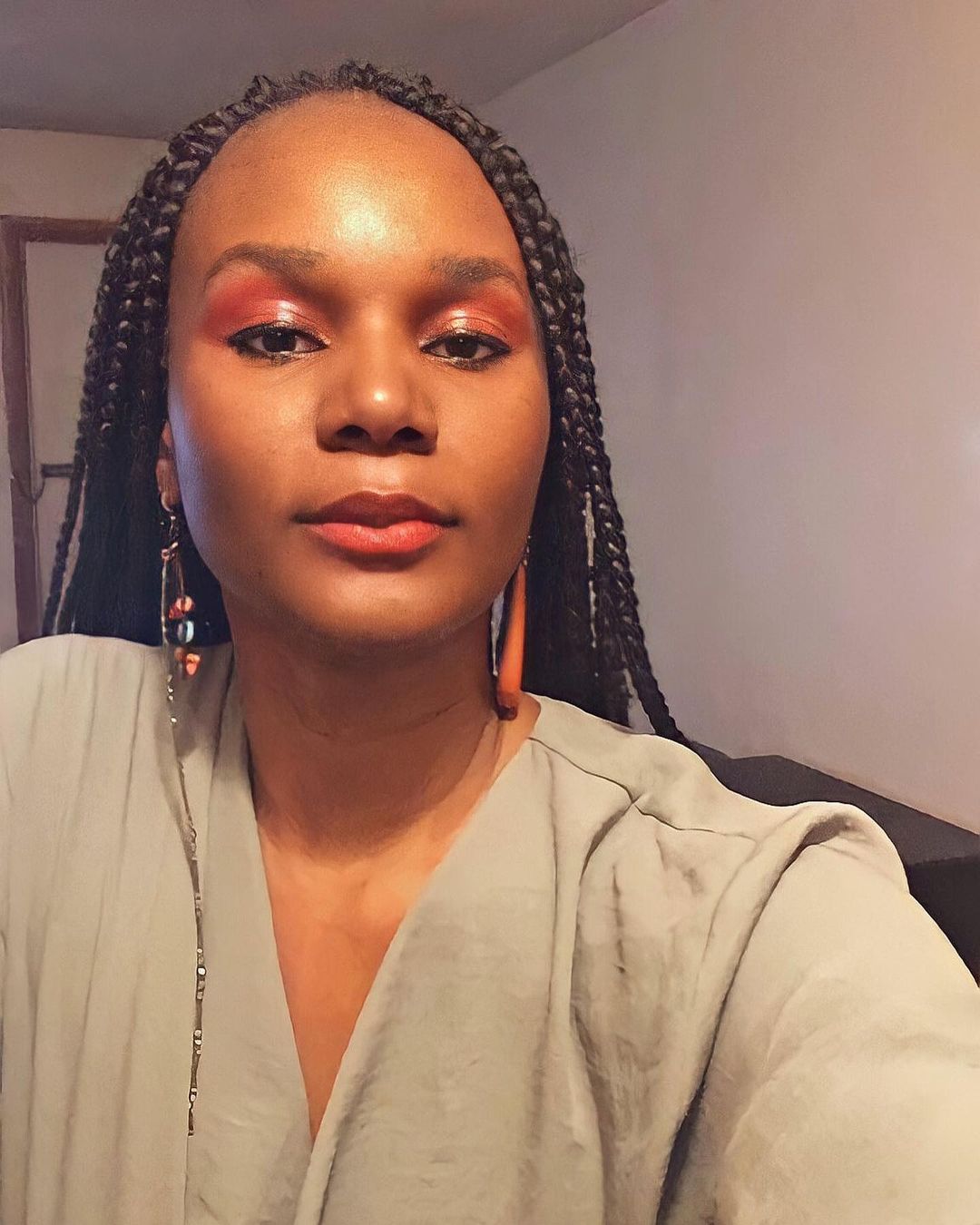

So this is how to tell the African story: tell all.
“Whenever I go to the village, women would gather around to peel egusi. It’s like a communion activity but that’s where the hottest gossip is going on – they’re finishing everybody in the society. By the time they’re done, you, who came to visit, would leave with a wealth of stories. I want to read a story set in that commune. I want to read gossip. The African story shouldn’t be boxed; tell all kinds of stories. Be experimental, go outside your norm, and make these stories richer.”
There is no ‘African story.’ Don’t hyperfocus on a particular theme or story and make it the African story. Don’t amplify only men’s voices, present them as the only ones capable of being experts, and leave out women’s voices. Uka says we should “Publish women; every woman. Read women, broadcast women, fund women, give women the spotlight.”
We are all storytellers, so this is how you can also tell the African story: read, share, contribute, and donate to literary magazines. Use whatever resource you can to louden the voices of writers and storytellers.
***
Many thanks to Ukamaka Olisakwe for being a part of this series. You can make donations to Isele Magazine by visiting the Isele website. You can also purchase Ogadinma here and here.